For high volume servers we recommend switching from the default MySQL storage back end to the the Redis back end for Bayes data. This allows spam training and Bayes lookups to run in memory which makes it extremely fast.
Export the Current Bayes Data
Run the sa-learn command below to export the Bayes data that is stored in the MySQL database to a file that you can use later to import back into the Redis database:
sa-learn -u amavis --backup > /tmp/amavis-bayes.dbInstall Redis
Important: It is up to you to secure your Redis installation. You should make sure that the Redis port 6379 is not exposed to the Internet. We recommend binding Redis to the IPv4 loopback interface 127.0.0.1 (normally this is done by default) and setting a password for it. Also Redis is an in memory storage engine so you must have the free memory available on the server. (A typical server will use under 100MB of bayes data while a really busy server could use over 1 GB of memory.)
RHEL/Centos/Cloudlinux/AlmaLinux
yum install redis
systemctl enable redis --now Debian/Ubuntu
apt-get install redis-server
systemctl enable redis-server --now Enable Redis in Warden
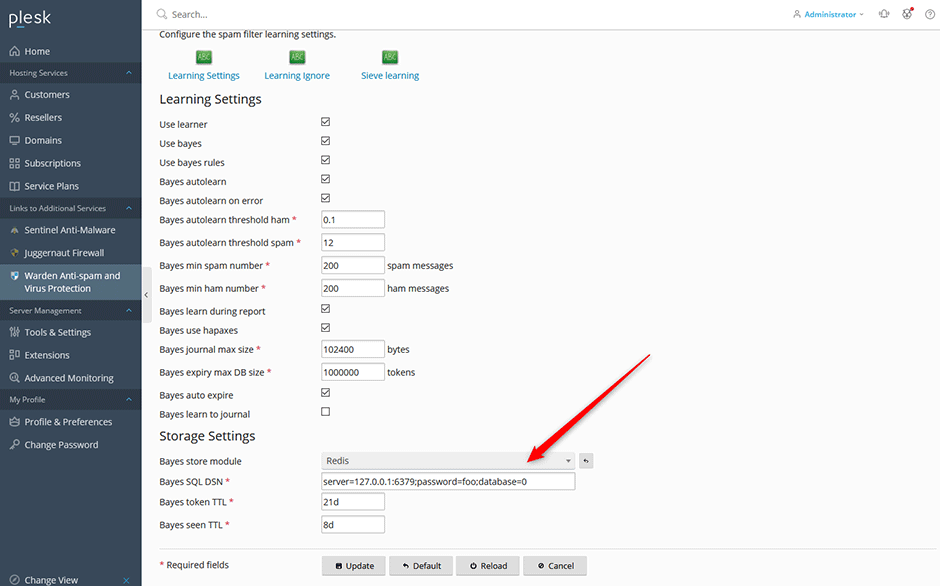
- Go to Warden -> Settings -> Learning Settings and change the Bayes store module option to Redis.
- Enter in the Redis password if you are using one in the Bayes SQL DSN.
- Enter in the Bayes Token TTL (The number of days before the entries expire). For low volume servers we recommend 180d (6 months). For high volume servers we recommend 90d (3 months).
- Press the update button to save your settings.
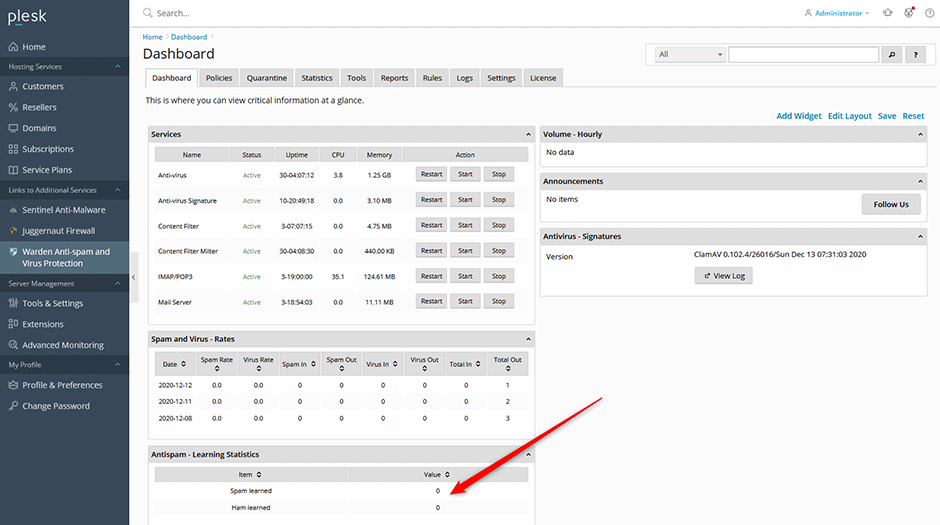
If everything is working you should see the Anti-spam learning dashboard widget reset to zero and it should increment throughout the day as the real-time learning, auto learning, and nightly training runs.
Import the Exported Bayes Data Back into Redis
Run the sa-learn command below to import the exported Bayes data back into the Redis database:
sa-learn -u amavis --restore /tmp/amavis-bayes.db
